How Can Hotel Hot Tubs Meet the Unique Challenges of the Middle East?
2024-11-05 11:22:44
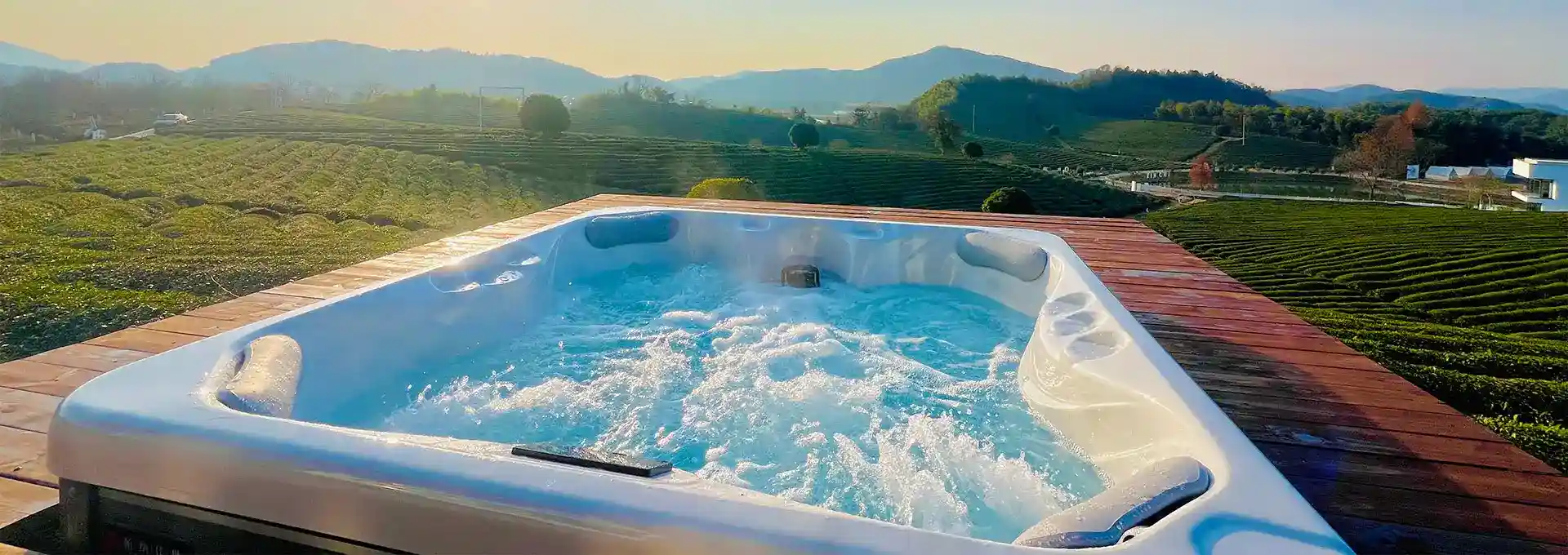
The Middle East has seen a surge in luxury hospitality over the past decade. High-end hotels and resorts are constantly seeking new ways to attract discerning guests and provide unique experiences. One amenity that has gained popularity is the hot tub, offering a relaxing and indulgent escape from the desert heat.
In a region known for its scorching temperatures, hot tubs might seem counterintuitive. However, they provide a refreshing contrast to the dry climate, especially during cooler evenings. The therapeutic benefits of hydrotherapy, combined with the social aspect of hot tubs, make them an attractive feature for both leisure and business travelers.
Despite their appeal, hot tubs in the Middle East face unique challenges. The region's harsh environment, limited water resources, and cultural considerations all play a role in shaping the way hotels approach hot tub installations and maintenance. This article explores these challenges and presents innovative solutions for hoteliers looking to incorporate hot tubs into their Middle Eastern properties.
Water Quality and Conservation: A Prime Concern
Water scarcity is a critical issue in many Middle Eastern countries. The World Resources Institute reports that 12 out of the 17 most water-stressed countries in the world are in the Middle East and North Africa region. This scarcity poses a significant challenge for hotels looking to offer water-based amenities like hot tubs.
Maintaining water quality in hot tubs is crucial for guest safety and enjoyment. The warm water environment can be a breeding ground for bacteria and other microorganisms if not properly managed. In the Middle East's hot climate, this challenge is amplified. Higher temperatures accelerate chemical reactions and bacterial growth, requiring more frequent water testing and treatment.
The arid climate also leads to rapid evaporation, which can concentrate contaminants in the water. This not only affects water quality but also increases water consumption as hot tubs need to be refilled more frequently. Hotels must strike a delicate balance between providing a luxurious experience and conserving water resources.
To address these challenges, hotels are turning to advanced water treatment systems and implementing strict water management protocols. Some properties are exploring the use of saltwater systems, which can reduce chemical usage and improve water quality. Others are investing in high-efficiency filtration systems that can extend the life of the water in the hot tub, reducing the frequency of complete water changes.
Advanced Water Treatment and Filtration Systems
The unique environmental conditions of the Middle East necessitate advanced water treatment solutions for hotel hot tubs. Traditional chlorine-based systems, while effective, may not be sufficient to handle the increased bacterial load and rapid chemical depletion caused by high temperatures and intense sunlight.
One innovative approach is the use of ozone treatment systems. Ozone is a powerful oxidizer that can eliminate a wide range of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, and organic compounds. It's particularly effective in hot water environments and can significantly reduce the need for traditional chemical treatments. A study published in the Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering found that ozone treatment can reduce chemical usage in swimming pools by up to 80%, which could translate to similar benefits for hot tubs.
Another promising technology is UV-C disinfection. UV-C light inactivates microorganisms by disrupting their DNA, preventing them from reproducing. When combined with traditional filtration methods, UV-C systems can provide an additional layer of protection against waterborne pathogens. This is especially valuable in the Middle East, where the warm climate can accelerate microbial growth.
Advances in filtration technology are also helping hotels maintain water quality while conserving resources. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems, typically used in air purification, are being adapted for water treatment. These systems can remove particles as small as 0.3 microns, ensuring crystal-clear water with minimal chemical intervention.
The integration of smart sensors and automated monitoring systems allows hotels to maintain optimal water quality with reduced manual intervention. These systems can continuously monitor parameters such as pH, chlorine levels, and temperature, adjusting treatment protocols in real-time to maintain ideal conditions.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
The Middle East's unique environmental conditions present several challenges for hot tub maintenance in hotels. One of the most significant issues is mineral buildup and scale formation due to the region's hard water. The high mineral content, particularly calcium and magnesium, can lead to deposits on surfaces and equipment, reducing efficiency and potentially damaging components.
To combat this, hotels are implementing water softening systems and using scale inhibitors. Regular descaling procedures are also crucial to prevent long-term damage and maintain energy efficiency. Some properties are exploring the use of electromagnetic water treatment devices, which claim to alter the crystal structure of minerals, preventing them from forming scale.
Energy efficiency is another critical consideration, given the high costs of cooling in the region. Hot tubs require constant heating, which can be energy-intensive. To address this, hotels are investing in high-efficiency heat pumps and exploring the use of solar heating systems to supplement traditional energy sources. Insulated covers are also being used to reduce heat loss and evaporation when the hot tubs are not in use.
Proper staff training is essential for managing hot tubs in Middle Eastern conditions. Employees need to understand the unique challenges posed by the climate and be proficient in using advanced treatment systems. Regular training sessions and partnerships with water treatment specialists can help ensure that staff are equipped to maintain hot tubs to the highest standards.
Cost-effective maintenance strategies are crucial for luxury hotels looking to offer hot tubs without compromising their bottom line. This includes implementing preventive maintenance schedules to catch issues before they become costly problems and using data analytics to optimize chemical usage and energy consumption.
Future Trends and Innovations in Middle Eastern Hotel Hot Tubs
The future of hotel hot tubs in the Middle East is likely to be shaped by emerging technologies and a growing emphasis on sustainability. One promising area is the development of biological water treatment systems. These systems use beneficial bacteria to break down contaminants, potentially reducing the need for harsh chemicals. Research published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering suggests that biological treatment can be highly effective in removing organic compounds from water, with potential applications in recreational water facilities.
Nanotechnology is another field with potential applications in hot tub water treatment. Nanofilters and nanomaterials with antimicrobial properties could provide more efficient and targeted water purification. A review in the Journal of Nanomaterials highlights the potential of nanosilver and other nanomaterials in water disinfection, offering new possibilities for maintaining water quality in challenging environments.
Sustainable practices are becoming increasingly important in the hospitality industry, and hot tub operations are no exception. Hotels are exploring ways to recycle and reuse hot tub water, such as using it for landscape irrigation after appropriate treatment. Some properties are also investigating the use of saltwater systems, which can reduce chemical usage and provide a more natural bathing experience.
The integration of smart technology is set to revolutionize the guest experience in hotel hot tubs. IoT-enabled systems can allow guests to control temperature, jets, and lighting from their smartphones. Some hotels are experimenting with aromatherapy systems that can be customized to individual preferences, enhancing the relaxation experience.
In conclusion, while hotel hot tubs in the Middle East face unique challenges, innovative technologies and thoughtful management practices are making it possible to offer this luxury amenity sustainably and efficiently. By embracing advanced water treatment systems, implementing rigorous maintenance protocols, and staying abreast of emerging trends, hotels can provide guests with a safe and enjoyable hot tub experience while respecting the region's environmental constraints.
One company at the forefront of addressing these challenges is Shenzhen Iparnassus Intelligent Spas Co., LTD. Specializing in holiday hot tubs and endless swim spas, their products are equipped with advanced circulating filtration and bacteria elimination systems. These features are particularly valuable in the Middle Eastern context, where reducing the frequency of water changes is crucial for conservation efforts.
With a professional team dedicated to design, research and development, production, sales, and after-sales service, Iparnassus has secured over 30 patents as of 2023. Their commitment to innovation positions them well to meet the unique demands of the Middle Eastern market. The iParnassus® brand's global reach, spanning dozens of countries and regions worldwide, demonstrates their ability to adapt their high-quality products to diverse environmental conditions.
As the hospitality industry in the Middle East continues to evolve, companies like Iparnassus will play a crucial role in providing solutions that balance luxury with sustainability. Their focus on conveying a syncretic lifestyle that combines spa culture with unique Chinese influences offers an intriguing proposition for Middle Eastern hotels looking to differentiate their offerings in a competitive market.
The future of hotel hot tubs in the Middle East looks promising, with technology and sustainability driving innovation. As the region continues to establish itself as a global luxury tourism destination, the ability to offer world-class amenities like hot tubs, while respecting local environmental and cultural considerations, will be a key factor in the success of high-end hotels and resorts.
For more information on hot tub installations and to find out more about our products, please feel free to contact us at info@iparnassus.com.
References:
1. World Resources Institute. (2019). 17 Countries, Home to One-Quarter of the World's Population, Face Extremely High Water Stress.
2. Naddeo, V., Rizzo, L., & Belgiorno, V. (2011). Water, wastewater and soil treatment by advanced oxidation processes (AOPs): A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 175, 1-7.
3. Chowdhury, S., Alhooshani, K., & Karanfil, T. (2014). Disinfection byproducts in swimming pool: Occurrences, implications and future needs. Water Research, 53, 68-109.
4. Hijnen, W. A. M., Beerendonk, E. F., & Medema, G. J. (2006). Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo)cysts in water: A review. Water Research, 40(1), 3-22.
5. Boucherit, A., Moulay, S., Ghernaout, D., Al-Ghonamy, A. I., Ghernaout, B., Naceur, M. W., ... & Messaoudene, N. A. (2015). New trends in disinfection by-products formation upon water treatment. Journal of Research & Developments in Chemistry, 2015, 1-27.
6. Li, Q., Mahendra, S., Lyon, D. Y., Brunet, L., Liga, M. V., Li, D., & Alvarez, P. J. (2008). Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential applications and implications. Water Research, 42(18), 4591-4602.
7. Lazarova, V., & Bahri, A. (2004). Water reuse for irrigation: agriculture, landscapes, and turf grass. CRC Press.
8. Zwiener, C., Richardson, S. D., De Marini, D. M., Grummt, T., Glauner, T., & Frimmel, F. H. (2007). Drowning in disinfection byproducts? Assessing swimming pool water. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(2), 363-372.